Cross validation example with multiple classifiers
This example runs cross validation and shows confusion matrix using multiple classifiers
- For CoSMoMVPA's copyright information and license terms, #
- see the COPYING file distributed with CoSMoMVPA. #
Contents
Define data
config = cosmo_config(); data_path = fullfile(config.tutorial_data_path, 'ak6', 's01'); data_fn = fullfile(data_path, 'glm_T_stats_perrun.nii'); mask_fn = fullfile(data_path, 'vt_mask.nii'); ds = cosmo_fmri_dataset(data_fn, 'mask', mask_fn, ... 'targets', repmat(1:6, 1, 10), ... 'chunks', floor(((1:60) - 1) / 6) + 1); % remove constant features ds = cosmo_remove_useless_data(ds);
Define classifiers in a cell
>@@>
classifiers = {@cosmo_classify_nn, ...
@cosmo_classify_naive_bayes, ...
@cosmo_classify_lda};
% if svm classifier is present (either libsvm or matlab's svm), use that
% too
if cosmo_check_external('svm', false)
classifiers{end + 1} = @cosmo_classify_svm;
end
% <@@<
nclassifiers = numel(classifiers);
Define partitions
partitions = cosmo_nfold_partitioner(ds);
Run classifications
Compute the accuracy and predictions for each classifier, and plot the confusion matrix
for k = 1:nclassifiers classifier = classifiers{k}; % get predictions for each fold, and store the result in % a variable 'pred'. % This output is in a 60 x 10 matrix, corresponding to predictions % for all 60 samples and 10 folds % >@@> pred = cosmo_crossvalidate(ds, classifier, partitions); % <@@< % use cosmo_confusion_matrix to compute the confusion matrix for each % fold, and store the results in a variable 'confusion_matrix_folds'. % The output is 6 x 6 x 10, consisting of 10 confusion matrices each % of size 6 x 6 % >@@> confusion_matrix_folds = cosmo_confusion_matrix(ds.sa.targets, pred); % <@@< % sum the confusion matrix_folds alnog the third dimension to % obtain a single 6 x 6 confusion matrix. Store the result % in a variable named confusion_matrix % >@@> confusion_matrix = sum(confusion_matrix_folds, 3); % <@@< % show the confusion matrix figure(); imagesc(confusion_matrix, [0 10]); accuracy = sum(diag(confusion_matrix)) / sum(confusion_matrix(:)); title(sprintf('%s: %.3f', strrep(func2str(classifier), '_', ' '), accuracy)); end
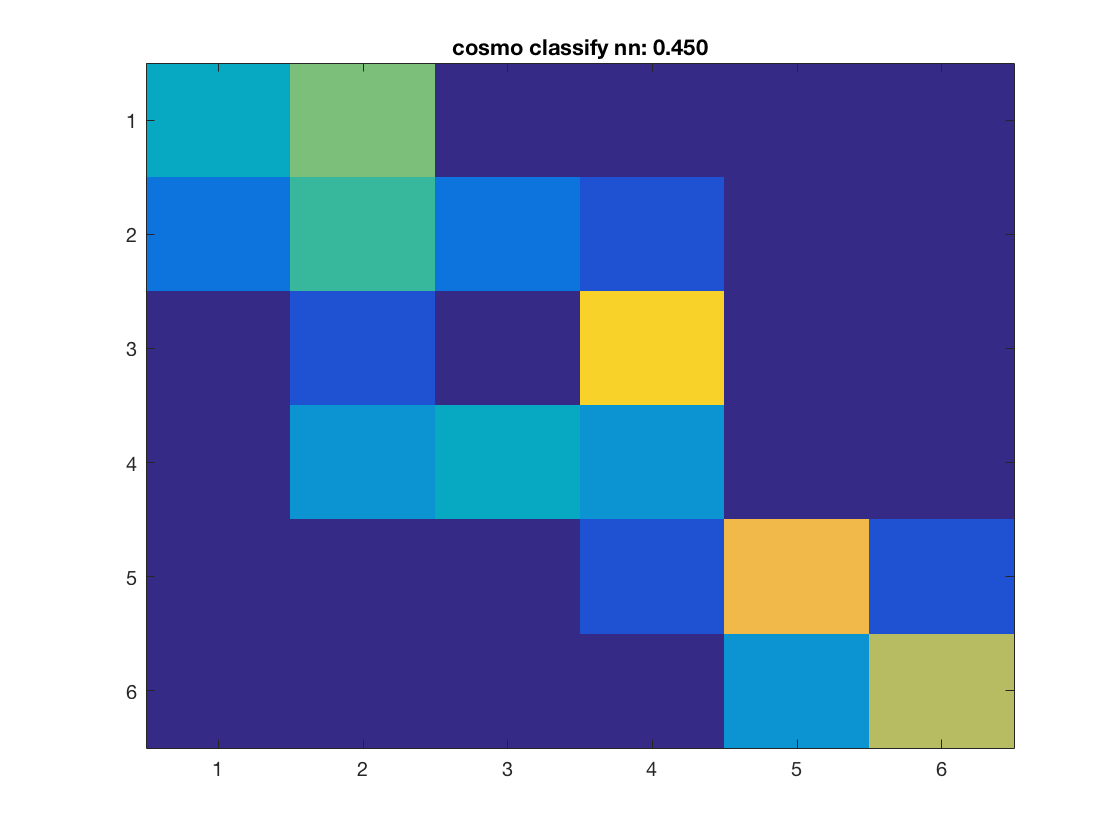
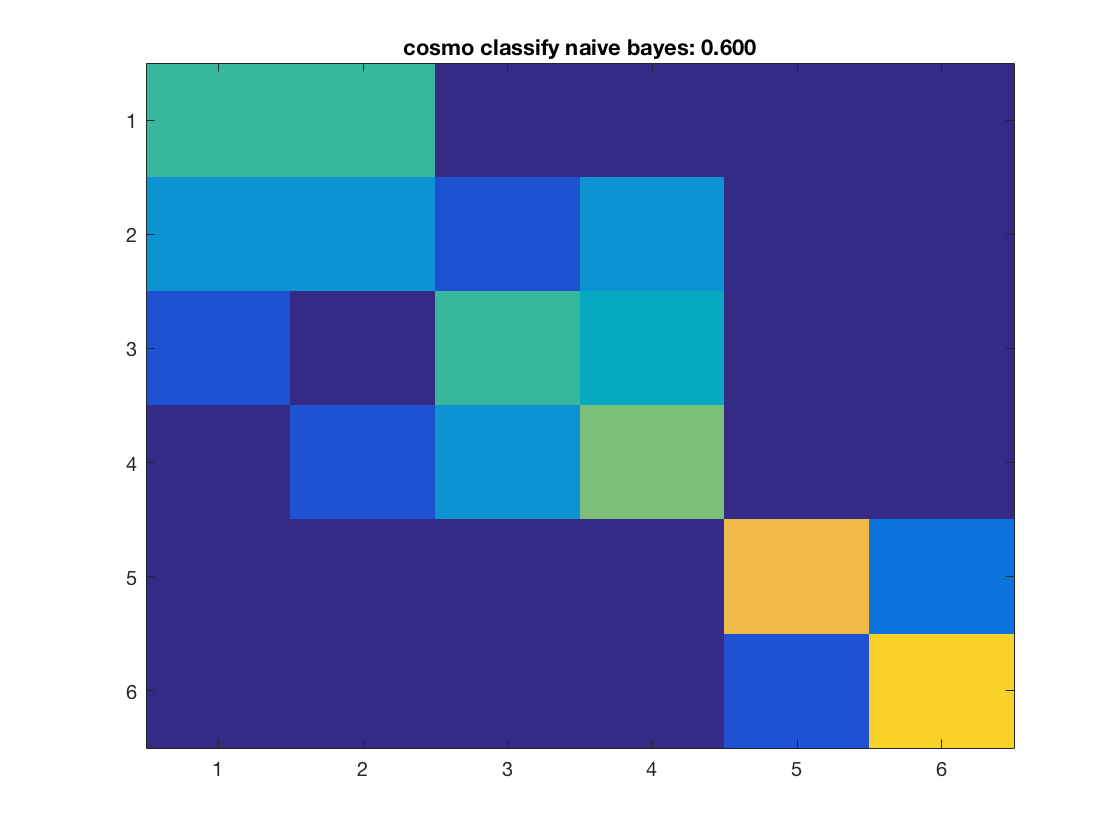
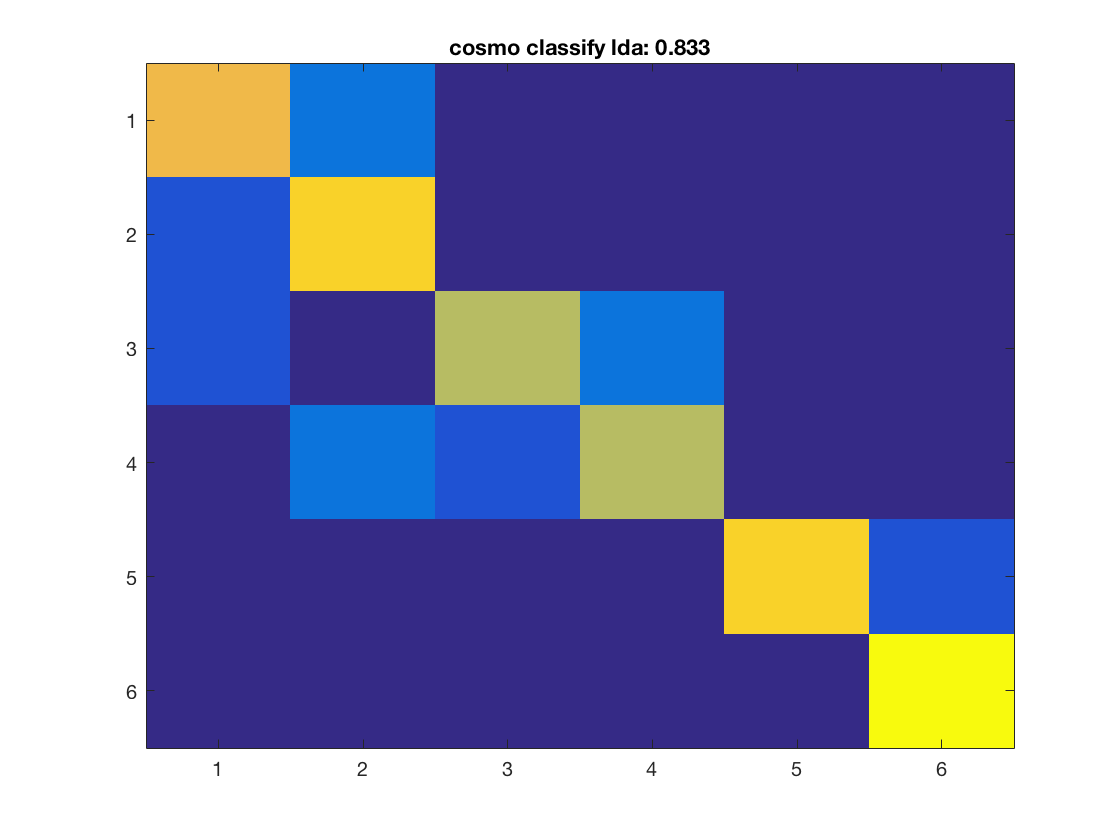
Consider effect or normalization
normalizations = {'zscore', ...
'demean', ...
'scale_unit', ...
'none'};
for k = 1:nclassifiers
classifier = classifiers{k};
classifier_name = strrep(func2str(classifier), '_', ' ');
for j = 1:numel(normalizations)
opt = struct();
opt.normalization = normalizations{j};
[pred, accuracy] = cosmo_crossvalidate(ds, classifier, partitions, opt);
fprintf('%s with %s-normalization: %.3f\n', classifier_name, ...
opt.normalization, accuracy);
end
end
cosmo classify nn with zscore-normalization: 0.417 cosmo classify nn with demean-normalization: 0.450 cosmo classify nn with scale_unit-normalization: 0.450 cosmo classify nn with none-normalization: 0.450 cosmo classify naive bayes with zscore-normalization: 0.600 cosmo classify naive bayes with demean-normalization: 0.600 cosmo classify naive bayes with scale_unit-normalization: 0.600 cosmo classify naive bayes with none-normalization: 0.600 cosmo classify lda with zscore-normalization: 0.850 cosmo classify lda with demean-normalization: 0.833 cosmo classify lda with scale_unit-normalization: 0.817 cosmo classify lda with none-normalization: 0.833